09 Jan 2023
More of us are vulnerable to the effects of flooding than ever before due to changes in climate, land use, infrastructure and population growth in recent decades. It is, therefore, crucial to accurately predict flood frequency and severity to reduce physical and economic losses.

Flooded lake house, Keswick, Cumbria, UK (Photo by Gavin Lynn)
Conventional analysis of flood frequency assumes that flooding follows historic patterns, and the methods used often do not take into account changing conditions such as climate change, river regulation, and land cover variation. This creates a higher risk of underestimating the frequency and severity of floods and designing less resilient infrastructure.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Hydrology, researchers from Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, China; Chung-Ang University, Korea; and the University of Liverpool, UK, proposed that an alternative method is more appropriate for analysing flood frequency in a changing environment.
The team of researchers propose a model that is a type of nonstationary flood frequency analysis. Nonstationary models provide more reliable estimations for water-related structures and flood prevention measures as they take into account variations of factors influencing flood frequency.
Despite nonstationary flood frequency analysis now being a hot research topic, there is a lack of consensus on the most appropriate methods. The existing models are either too complicated or too expensive for engineers or hydrologists to implement in practice.
Mengzhu Chen, the first author of the paper, is a PhD student at XJTLU’s Department of Civil Engineering. Back in 2021, she published a study that used a different model of nonstationary flood frequency across the UK. However, she found there were limitations in applying this approach to practices like engineering design and hydraulic structure design.
“We were unable to express the model as a simple mathematical formula which made it difficult to interpret and calculate. Therefore, we wanted to find a more suitable model,” Chen says.
To assess and compare different modelling techniques in the current study, the researchers analysed historical flood data from 161 catchments across the UK. These areas, also known as watersheds or drainage basins, have natural boundaries such as ridges, hills or mountains, and all surface water drains to a common channel to form rivers or creeks.
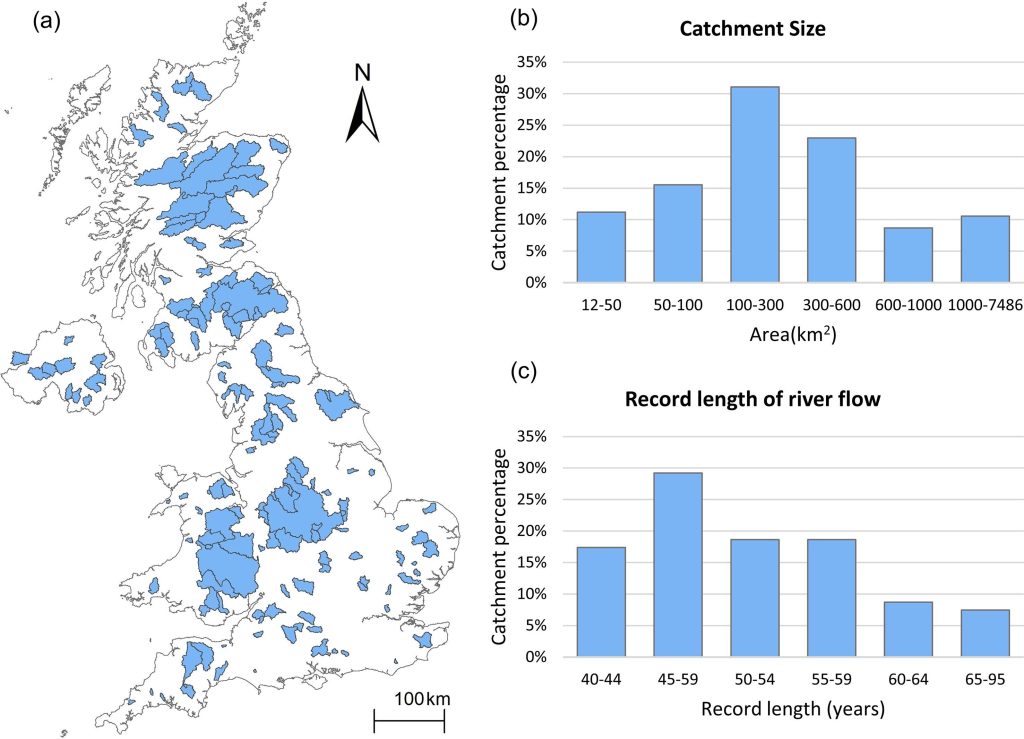
(a) Location of the 161 catchments used in the study. (b) Summary of catchment size and (c) available record length.
They found that the ‘fractional polynomial-based regression’ model is the most flexible, effective, and user-friendly among all the models. This method is an emerging tool in certain applied research areas like medical statistics and clinical research but is currently used very little in the hydrology field.
Bridging the gap
Chen says: “Currently, there is a gap between hydraulic research and practice, as most practitioners are not familiar with nonstationary models even though they have gained popularity in academia.
“The findings of our recent study provide recommendations to hydrologists and engineers to help them choose from the available analysis models.
“For practitioners, the fractional polynomial model we propose in our paper can be an additional valuable tool for application. It can be expressed as a mathematical formula and is more user-friendly.
“After all, the primary purpose of nonstationary flood frequency analysis is to provide estimations for the design, construction, and management of water-related infrastructure.
“Nevertheless, there’s a long way to go before nonstationary methods can be widely used in practice. A more user-friendly, straightforward, and generally agreed-upon approach for nonstationary flood frequency analysis is still worth exploring in the future,” Chen says.
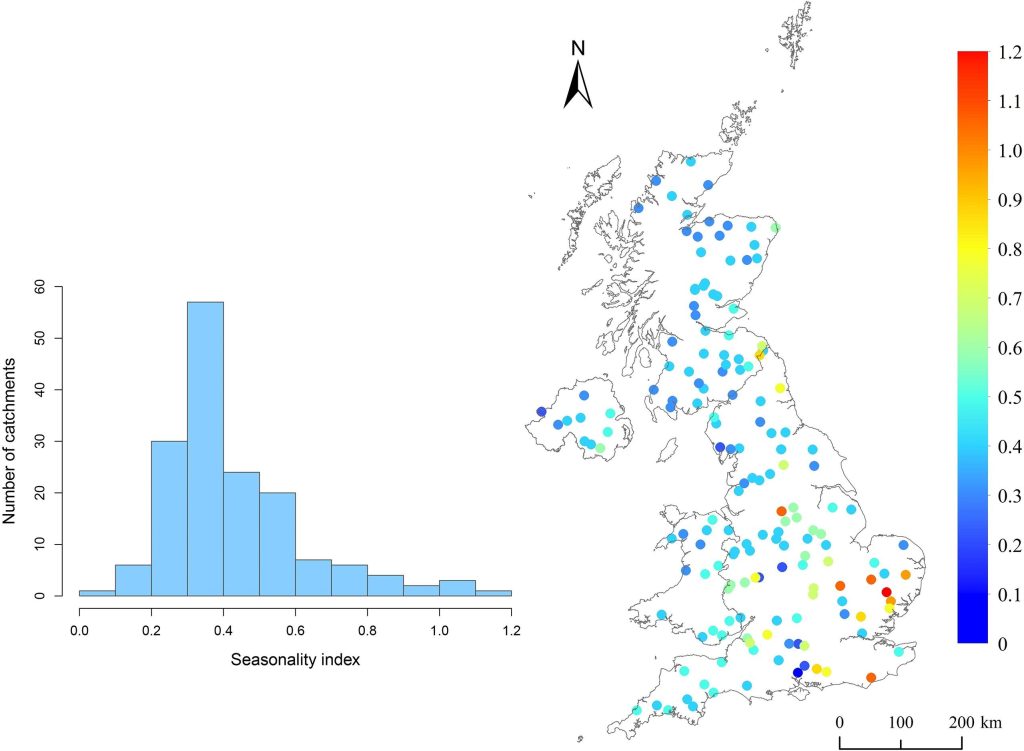
Quantified seasonality index (seasonal flood peak variance) for the 161 catchments across the UK. The higher the index, the more significant the flood variability is in these catchments; the wet season may be wetter, and the dry season may be drier.
“We also need further investigation into the complex underlying factors influencing flood frequency to help prepare for future extreme weather events,” she adds.
The research team consists of Mengzhu Chen and Professor Konstantinos Papadikis from XJTLU, Dr Changhyun Jun from Chung-Ang University, and Professor Neil Macdonald from the University of Liverpool.
The paper, Linear, nonlinear, parametric and nonparametric regression models for nonstationary flood frequency analysis, is available online here.
By Yi Qian
Edited by Catherine Diamond
09 Jan 2023
RELATED NEWS

XJTLU study exposes increasing flood risk in the UK
As climate change continues to cause unpredictable and extreme weather events around the world, Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University researchers are calling f...
Learn more

Digital transformation in construction industry requires more support, study shows
In recent years, the engineering and construction industries have been exploring the use of digital technologies to boost productivity and improve safety, qu...
Learn more
Researchers use bacteria to enhance concrete resistance
Concrete, with its low cost, good in compressive strength, and manufacturing convenience, is one of the most widely used materials in construction. However, ...
Learn more








