20 Aug 2025
Two student teams from XJTLU’s School of Advanced Technology won Grand and Second Prizes at the Sixth Jiangsu Province Biomedical Engineering Innovation Design Competition with their rehabilitation products. By combining games, traditional Chinese medicine, and Internet of Things (IoT) technology, the teams aim to make rehabilitation training more engaging, accurate, and trackable.

Students from XJTLU’s School of Advanced Technology
The Grand Prize-winning project is an intelligent carpet for lower limb rehabilitation training in children with cerebral palsy. It combines embedded hardware, IoT communication, game-based training, and gait assessment technology to collect accurate data while keeping users engaged.
The second award-winning project is an smart medical splint system, which is a type of brace for supporting fractures, with monitoring, data analysis, and remote management abilities, designed to support treatments of common radius fractures in older people.
Game-based rehabilitation
Professor Jie Sun, Head of the Department of Mechatronics and Robotics, said that traditional rehabilitation methods are often seen as repetitive and boring, leading many children with cerebral palsy to resist training. To address this, the team designed two games for the carpet, “Whack-a-Mole” and “Pressure Control” using real-time lighting, voice prompts, and positive feedback to guide children. They also included a two-player mode to make training more social and fun.
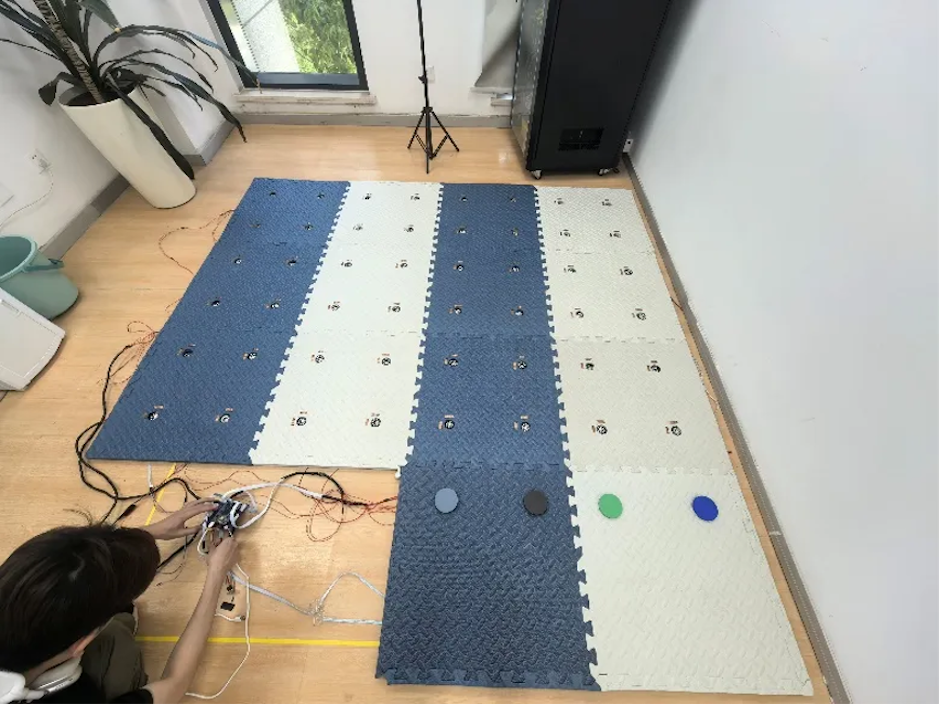

Installation of the smart carpet
“Gait assessment is central to such rehabilitation training, but traditional methods rely on human observation, which can lead to big errors,” Professor Sun notes. “To address this, we adopted a unique structural design and embedded advanced sensors into the carpet, creating a comprehensive intelligent system.”
The system tracks body movements and pressure with about 95% accuracy, creating a loop of training, assessment, and plan updates. Data can be easily checked through a WeChat mini-program, so family members and doctors can follow progress and adjust training.
“This project is a prime example of medical-engineering integration. It showcases the practical efforts of young students to apply technological innovation for the benefit of society and the improvement of people’s livelihoods,” says Professor Sun.
The system has been tested at BenQ Medical Center in Suzhou and received positive feedback from medical staff and families.
Smart splints for rehabilitation
Traditionally, doctors use splints to keep fractures still and judge recovery mainly by experience, as progress cannot be monitored in real time. To solve this, XJTLU student team noted problems such as no clear standards and no dynamic feedback. They proposed a new solution combining traditional Chinese splint therapy with modern IoT technology.
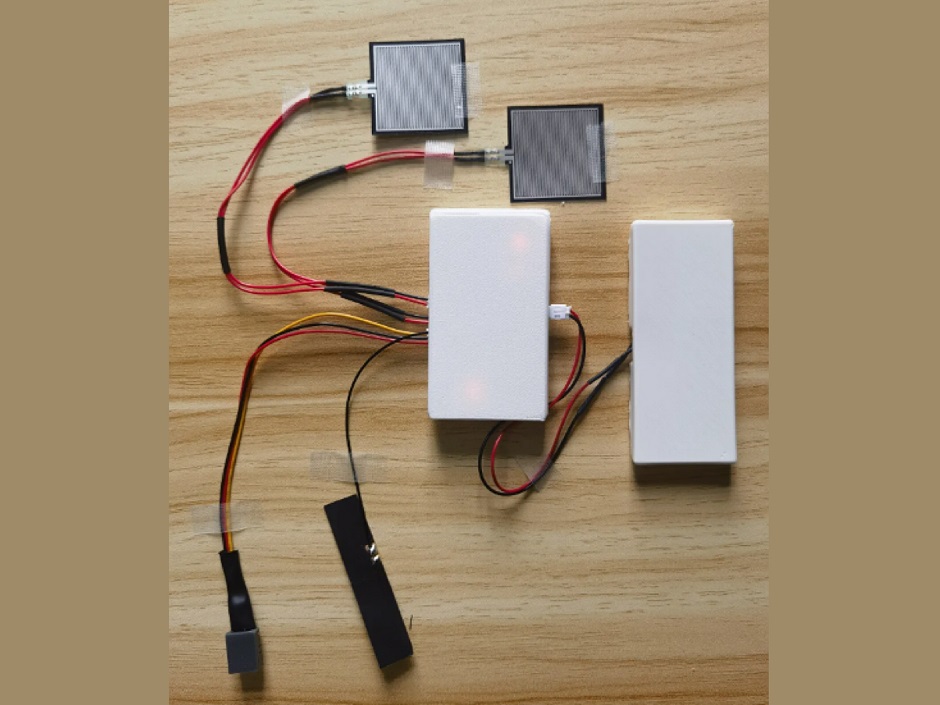
Core components of the smart splint, including sensors, batteries, and main control boards
The team embedded smart sensors into a splint to monitor pressure, temperature, humidity, and posture at the fracture site in real time. Data is uploaded to the cloud via an IoT module and displayed on a management platform with early warning functions. The system has been tested for stability and data reliability, and in preclinical trials with Suzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, early results showed it could track recovery progress and predict short-term outcomes.
Dr Qinglei Bu, the team’s supervisor from the Department of Mechatronics and Robotics, says, “Our project transforms the experiential theory of traditional Chinese bone-setting into quantifiable real-time data. This interdisciplinary approach offers a new solution for rehabilitation in elderly patients with fractures and contributes to the digital transformation of orthopaedic rehabilitation and the modernisation of Chinese medicine.”
Winner List:
Grand Prize: A Customisable Lower Limb Rehabilitation Carpet for Children
Team Members: Keming Zhang, Ziyang Kan, Yaxuan Liu, Chengqi Song
Advisors: Jie Sun, Yongqi Liang (National University of Singapore Suzhou Research Institute)
Second Prize: Smart Medical Splints
Team Members: Siyuan Wang, Zheng Yan (Suzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Shuchen Liu, Zheng Jin, Yiheng Ren
Advisors: Qinglei Bu, Jintao Liu (Suzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine)
By Huatian Jin
Translated by Xueqi Wang
Edited by Ziling Yang and Xinmin Han
Photos courtesy of School of Advanced Technology
20 Aug 2025
RELATED NEWS

How AI Optimises VR Museum Displays for Comfort
In traditional museums, the height of exhibits, viewing distance, and tools like magnifying glasses are carefully designed to enhance the viewing experience....
Learn more

XJTLU projects on bird flight paths, AI music impress at CHI 2025
Innovative projects to untangle the complex flight paths of migratory birds and build an AI music creation system earned Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University ...
Learn more








